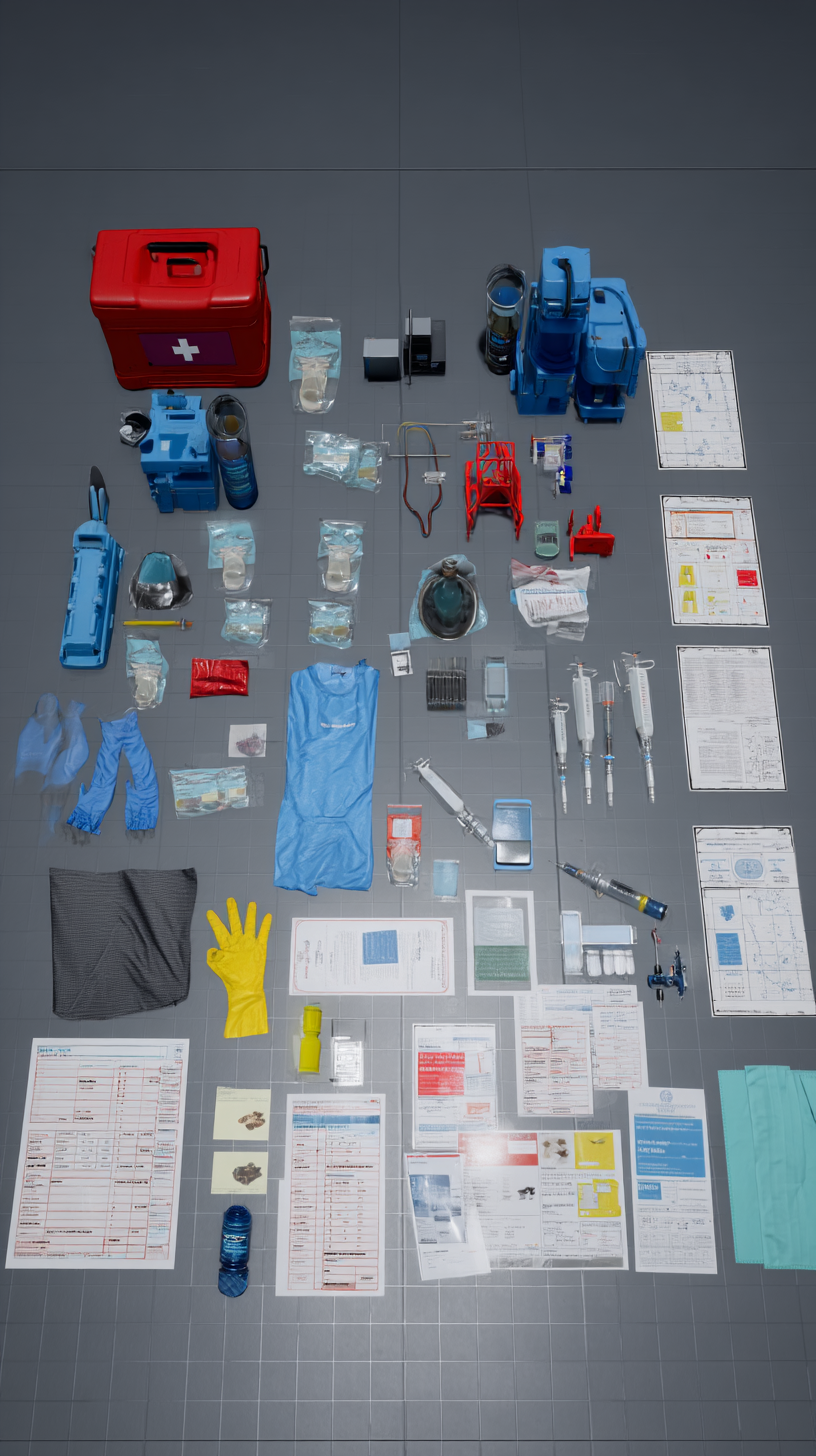
XR Nursing Training / Pack-1
Pack-1 / Beginner Level Learning Outcomes
This module introduces foundational clinical competencies for nursing students and early-career professionals through immersive, scenario-based simulations. Each outcome is linked to standardized nursing education frameworks and reflects realistic challenges faced in emergency and acute care settings.
Emergency Response Competencies:
Scene Assessment: Learn to conduct rapid primary and secondary surveys in emergent environments.
Risk Mitigation: Understand the principles of safety for self, team, and patients in high-stress conditions.
First Aid Proficiency: Apply evidence-based first-aid interventions including bleeding control, airway management, and stabilization of trauma injuries.
Team Coordination: Practice interprofessional communication and task delegation under pressure.
Triage & Mass Casualty Management:
Triage Classification: Develop the ability to assess and categorize patients based on acuity using standardized color-coded systems (START, SALT).
Resource Allocation: Train in decision-making under limited resource conditions to maximize patient outcomes.
Documentation & Communication: Accurately log findings and communicate patient status to supervising clinicians or emergency teams.
Pre-Hospital Transport Preparation:
Ambulance Protocols: Gain familiarity with preparing patients and equipment for ground or air medical transport.
Patient Handover: Practice structured handover communications (SBAR/IMIST-AMBO frameworks) with emergency department teams.
In-Transit Clinical Skills:
Monitoring & Intervention: Monitor vital signs and respond to deterioration using basic interventions within the constraints of transport environments.
Ergonomic Practice: Adapt to confined spaces and manage equipment safely in motion (e.g., during ambulance or helicopter transfer).
Safety Procedures: Implement patient and provider safety protocols during transfer operations.
Accident Scene Discovery
Scenario Type: Outdoor multi-victim trauma response
Learning Level: Beginner to Intermediate (pre-hospital focus)
Duration: 12–15 minutesScenario Overview
Trainees are deployed into a rural roadside environment, simulating the aftermath of a high-speed vehicular collision. Environmental stressors such as low visibility, uneven terrain, and ambient noise present realistic challenges. The goal is to develop calm, structured clinical thinking in unfamiliar settings.Trainees encounter multiple injured individuals with varying degrees of trauma. Time, safety, and resource management are central to the scenario.Core Learning Objectives
Scene Safety & Situational Awareness:
Assess for immediate dangers (e.g., fire risk, fuel leakage, unstable ground). Establish a safe operating zone before engaging patients.Initial Triage & Primary Survey:
Use ABCDE (Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure) to rapidly identify life-threatening conditions. Apply START triage where applicable.Basic First Aid & Stabilization:
Deliver immediate interventions such as bleeding control, C-spine precautions, and shock management using limited field equipment.Communication & Role Clarity:
Use clear verbal cues or hand signals to coordinate with team members. Call for advanced support using simulated radio or digital interfaces.Decision-Making Under Pressure:
Prioritize actions based on injury severity, resource availability, and environmental constraints. Practice calm, evidence-based responses to high-stress stimuli.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
VR HUD with environmental prompts and vitals overlay
Interactive virtual toolkit for selecting and using supplies
Optional real-time feedback system (for instructor-led training)
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Basic trauma kit (gauze, bandages, gloves, antiseptic)
Cervical collar, rescue blanket, flashlight
Radio and simulated dispatch interface
Patient triage tags (color-coded)
Scene hazard markers (virtual cones, flares)
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Timeliness and accuracy of patient assessment
Adherence to safety protocols
Team communication effectiveness
Quality of basic interventions and prioritization
Emotional regulation under pressure
On-Site Triage & Initial Treatment
Scenario Type: Multi-victim emergency triage zone
Learning Level: Beginner to Intermediate
Duration: 15–20 minutesScenario Overview
Building on the initial discovery phase, this simulation transitions to a structured triage environment. Trainees operate within a temporary field treatment zone established near the accident site. Multiple victims present with varied injury profiles, and trainees must manage prioritization, stabilization, and collaboration efficiently.This scenario introduces time pressure, limited supplies, and evolving patient conditions to reinforce critical thinking, leadership, and structured response under stress.Core Learning Objectives
Triage Execution (START/SALT):
Apply recognized triage frameworks to categorize patients according to injury severity and urgency of care. Assign appropriate tags and update them as conditions evolve.Field Stabilization Skills:
Practice intermediate first aid interventions such as hemorrhage control, splinting, IV line initiation, oxygen administration, and shock management.Time & Resource Management:
Allocate limited supplies across multiple victims. Balance speed with clinical precision in high-demand situations.Team-Based Coordination:
Develop clear roles and lines of communication within the care team. Practice directing others or following instructions depending on role assignment.Dynamic Reassessment:
Monitor victims for changes in condition and adjust priorities or interventions accordingly. Recognize deterioration and act decisively.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
VR triage tagging interface with drag-and-drop patient labeling
Wrist-mounted patient monitor showing basic vitals (pulse, respiratory rate, skin condition)
Voice-activated commands for teamwork simulation or instructor prompts
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Trauma kits (IV supplies, airway adjuncts, splints, dressings)
Portable oxygen and pulse oximeters
Cervical collars, safety gloves, surgical masks
Color-coded triage tents/zones
Patient charts and emergency intervention forms
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Accuracy of triage classification
Effectiveness of communication and leadership
Prioritization and sequencing of interventions
Correct usage of field equipment and PPE
Responsiveness to patient deterioration or unexpected events
Ground Ambulance Preparation
Scenario Type: Pre-hospital transport readiness
Learning Level: Intermediate
Duration: 10–15 minutesScenario Overview
This scenario immerses trainees in the critical transition from field stabilization to patient transport. Within a realistic virtual ambulance bay setting, learners must prepare both the patient and the ambulance environment for safe ground transport.Emphasis is placed on equipment setup, secure patient handling, and communication with receiving hospital teams. The simulation also highlights the physical and procedural constraints of mobile care environments.Core Learning Objectives
Equipment Familiarization:
Identify and prepare key medical devices commonly used in ambulances, including oxygen delivery systems, defibrillators, IV supplies, and immobilization tools.Patient Transfer Techniques:
Practice safe lifting, positioning, and securing of patients on a stretcher, including spinal immobilization when indicated.Ambulance Ergonomics & Space Management:
Organize supplies and patient positioning to maximize workflow and minimize risk inside the confined ambulance cabin.Communication with Receiving Facility:
Use simulated radio or digital devices to relay structured handoff reports (e.g., SBAR format) to the receiving emergency department.Safety Protocols & Rapid Readiness:
Implement scene safety checks, ensure all equipment is secure, and verify ambulance readiness for departure under time constraints.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
Touchscreen dashboard for communication with dispatch and hospital
VR inventory checklist for verifying readiness of essential devices and supplies
Interactive patient monitor showing vitals en route
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Transport stretcher with safety straps
Oxygen tanks, suction unit, AED
Trauma kit (dressings, splints, IV lines, emergency meds)
Communication tablet/radio unit
PPE including gloves, masks, and reflective vests
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Safety and accuracy during patient loading
Correct setup and use of critical ambulance equipment
Quality and clarity of hospital handoff communication
Efficiency in task execution under time pressure
Compliance with hygiene and safety protocols
Helicopter Evacuation Preparation
Scenario Type: Air medical coordination and patient transfer
Learning Level: Intermediate
Duration: 12–18 minutesScenario Overview
In this simulation, trainees operate within a rural emergency triage site as an incoming helicopter approaches for patient evacuation. The scenario focuses on safely preparing the landing zone, prioritizing evacuation candidates, and executing a smooth handover to flight medical crews.This training emphasizes communication across agencies, patient safety during rotorcraft operations, and adherence to standardized air transport protocols.Core Learning Objectives
Landing Zone Safety & Setup:
Identify and prepare a suitable landing zone (LZ), including wind orientation, debris clearance, marking, and personnel positioning in compliance with rotorcraft safety guidelines.Patient Evacuation Prioritization:
Apply clinical reasoning to determine which patients require air evacuation based on severity, transport time sensitivity, and available resources.Inter-agency Communication:
Coordinate with the flight crew and ground EMS using radio protocols and standardized terminology for safe, efficient transfers.Patient Transfer Handoff:
Execute structured handoff communications with the air medical team (e.g., MIST or IMIST-AMBO handoff models), detailing interventions to date, patient status, and anticipated needs.Rotorcraft Operational Awareness:
Observe and follow safety protocols related to helicopter operations, including approach/departure paths, rotor awareness, and noise protection.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
Virtual LZ guidance overlay and flare marker placement tool
Digital comms panel for coordinating ETA and patient handoff
Structured handover UI with real-time vitals and treatment summary
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Airlift-compatible stretcher
High-visibility safety vests, helmets, and goggles
Emergency flares, windsock, and LZ boundary markers
Medical documents: Air evacuation consent form, pre-transfer status chart
Hearing protection gear (noise-canceling headsets)
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Safety and correctness of landing zone preparation
Appropriateness of evacuation candidate selection
Clarity, completeness, and professionalism of medical handoff
Adherence to rotorcraft safety protocols
Overall coordination and leadership effectiveness
Helicopter Evacuation Preparation
Scenario Type: Air medical coordination and patient transfer
Learning Level: Intermediate
Duration: 12–18 minutesScenario Overview
In this simulation, trainees operate within a rural emergency triage site as an incoming helicopter approaches for patient evacuation. The scenario focuses on safely preparing the landing zone, prioritizing evacuation candidates, and executing a smooth handover to flight medical crews.This training emphasizes communication across agencies, patient safety during rotorcraft operations, and adherence to standardized air transport protocols.Core Learning Objectives
Landing Zone Safety & Setup:
Identify and prepare a suitable landing zone (LZ), including wind orientation, debris clearance, marking, and personnel positioning in compliance with rotorcraft safety guidelines.Patient Evacuation Prioritization:
Apply clinical reasoning to determine which patients require air evacuation based on severity, transport time sensitivity, and available resources.Inter-agency Communication:
Coordinate with the flight crew and ground EMS using radio protocols and standardized terminology for safe, efficient transfers.Patient Transfer Handoff:
Execute structured handoff communications with the air medical team (e.g., MIST or IMIST-AMBO handoff models), detailing interventions to date, patient status, and anticipated needs.Rotorcraft Operational Awareness:
Observe and follow safety protocols related to helicopter operations, including approach/departure paths, rotor awareness, and noise protection.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
Virtual LZ guidance overlay and flare marker placement tool
Digital comms panel for coordinating ETA and patient handoff
Structured handover UI with real-time vitals and treatment summary
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Airlift-compatible stretcher
High-visibility safety vests, helmets, and goggles
Emergency flares, windsock, and LZ boundary markers
Medical documents: Air evacuation consent form, pre-transfer status chart
Hearing protection gear (noise-canceling headsets)
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Safety and correctness of landing zone preparation
Appropriateness of evacuation candidate selection
Clarity, completeness, and professionalism of medical handoff
Adherence to rotorcraft safety protocols
Overall coordination and leadership effectiveness
Emergency Air-Evacuation
Scenario Type: Aeromedical transport – in-flight nursing care
Learning Level: Intermediate to Advanced
Duration: 10–15 minutesScenario Overview
In this immersive simulation, trainees are positioned inside a medical helicopter mid-flight, tasked with monitoring and stabilizing a critical trauma patient. The rotor noise, turbulence, and spatial constraints create a high-stakes environment demanding precision, adaptability, and confident decision-making.This scenario emphasizes practical in-flight medical skills, equipment handling, and continuous communication with the receiving facility.Core Learning Objectives
In-Flight Patient Monitoring:
Track vital signs using compact medical monitors. Respond promptly to signs of deterioration using appropriate interventions.Resource-Constrained Care Delivery:
Work with minimal equipment and limited mobility. Prioritize interventions effectively in a restricted setting.Stability & Safety Under Motion:
Maintain secure IV lines, airway devices, and equipment positioning despite flight movement. Ensure the patient and self are restrained and protected.Communication with Hospital Teams:
Transmit patient status updates to the receiving emergency department, including any new clinical developments or complications during transit.Collaborative Teamwork in Confined Spaces:
Coordinate actions efficiently with the onboard flight nurse or paramedic team, sharing responsibilities without error or delay.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
VR in-flight dashboard with real-time patient vitals
Voice-activated communication panel linked to hospital and pilot
Interactive tool panel with emergency medications and devices
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
In-flight defibrillator, suction unit, oxygen delivery kit
Portable IV infusion pump and emergency medication kit
Noise-adapted stethoscope and gloves designed for turbulence
Safety harnesses and mounted supply holders
Pre-filled handoff form synced to hospital records system
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Quality and accuracy of patient assessments under duress
Appropriate, prioritized use of in-flight medical resources
Consistency of communication with hospital and team
Adherence to safety procedures (self, patient, equipment)
Demonstrated confidence and calm under motion-related stress
In-Ambulance Care
Scenario Type: Pre-hospital patient management during ground transport
Learning Level: Intermediate
Duration: 10–15 minutesScenario Overview
This simulation places trainees inside a moving ground ambulance en route to the hospital. The patient, already triaged and partially stabilized, begins to show signs of clinical instability. Trainees must balance continual monitoring, timely interventions, and effective communication—all within a physically constrained, high-noise, mobile environment.The simulation reinforces applied clinical skills under motion and introduces the unique dynamics of delivering care during transport.Core Learning Objectives
Continuous Patient Monitoring:
Utilize portable devices to monitor vitals (HR, BP, O2 saturation) and detect early warning signs of deterioration.Medication Administration in Motion:
Safely administer IV fluids or emergency medications, ensuring correct dosages and documentation despite the movement.Securing Equipment & Environment:
Properly anchor all devices, maintain organized supplies, and ensure patient safety (seatbelts, head/neck support) while in transit.Communication with Receiving Facility:
Relay updated patient information to the hospital team using structured radio/telemetry communication. Prepare for a seamless transfer upon arrival.Stress Management & Clinical Judgement:
Stay focused in a confined, unpredictable setting. Prioritize interventions when patient condition changes en route.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
VR monitor interface with real-time vitals and alerts
Interactive MAR (Medication Administration Record) with dose selection and input logging
Comms tablet for handoff prep and hospital notifications
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Stretcher with restraint straps and elevation controls
IV drip setup, oxygen mask, suction device
Portable defibrillator and emergency med kit
Bag-valve mask (BVM) and trauma dressing kit
Waste bags, sanitizer, gloves, and PPE
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Accuracy of clinical interventions during transport
Maintenance of patient and equipment safety protocols
Quality of communication with receiving facility
Correct documentation of medications and care provided
Situational awareness and response to changes in patient condition
Hospital Arrival & Patient Transfer
Scenario Type: Pre-hospital to in-hospital care transition
Learning Level: Intermediate to Advanced
Duration: 8–12 minutesScenario Overview
In this phase, trainees execute the critical transition of patient care from field teams (ambulance or helicopter) to emergency department personnel. The scenario simulates either a hospital helipad or ER bay depending on the prior transport method.This simulation reinforces the importance of accurate communication, physical coordination, and procedural clarity under pressure.Core Learning Objectives
Safe Patient Transfer:
Use proper techniques for moving patients from stretcher to hospital bed, ensuring spinal protection, IV continuity, and oxygen flow.Structured Clinical Handoff:
Deliver a concise, structured report using recognized formats (SBAR, IMIST-AMBO), including injury mechanism, vitals, treatments given, and pending concerns.Coordination with Hospital Teams:
Recognize and adapt to hospital team workflows. Identify when to assist, when to brief, and when to step back.Documentation & Continuity of Care:
Transfer all relevant records, treatment summaries, and digital data to the ED team or EMR system. Ensure clarity, completeness, and HIPAA-compliant handling.Time-Sensitive Decision Making:
Recognize when immediate escalation (e.g., trauma activation, OR prep) is warranted based on observed deterioration or clinical handoff criteria.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
VR handoff interface with checklist prompts and vitals display
EMR transfer panel showing prior interventions and medications
Patient tracking system linked to bed assignment and triage priority
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Transfer stretcher and receiving hospital bed with side rail synchronization
IV stands, mobile monitors, and oxygen support
PPE for hospital and ambulance crews (gloves, masks, high-vis vests)
Printed or digital patient summary sheets
Consent documents, triage cards, and transport logs
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Safety and precision of patient handoff process
Clarity and accuracy of verbal and written reports
Appropriate urgency recognition and escalation
Professional interaction with hospital team
Completion of legal and administrative documentation
Emergency Room (ER) Integration
Scenario Type: Acute care admission and rapid clinical response
Learning Level: Intermediate to Advanced
Duration: 15–20 minutesScenario Overview
Trainees enter the emergency department alongside their patient and join the hospital team in managing a time-sensitive, high-acuity case. They must rapidly adapt from field care to hospital workflows, contributing meaningfully to diagnostics, stabilization, and treatment initiation under supervision.This scenario emphasizes situational awareness, interdisciplinary collaboration, and the ability to maintain composure and effectiveness in a dynamic clinical environment.Core Learning Objectives
ER Protocol Familiarity:
Understand emergency department layout, team roles, and procedural flow. Recognize trauma team activation and triage prioritization systems.Diagnostic Preparedness:
Participate in the early assessment phase—monitoring vitals, applying oxygen, starting diagnostics (labs, ECG), and reporting observations.Clinical Communication:
Engage in brief, accurate exchanges with physicians and nurses. Deliver situation updates, ask clarifying questions, and document key clinical data.Equipment Utilization:
Safely use ER monitoring and intervention tools, including cardiac monitors, IV medication systems, and airway adjuncts.Patient Advocacy & Safety:
Ensure the patient’s dignity, safety, and comfort throughout care. Monitor for pain, psychological distress, or signs of deterioration.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
ER team dashboard showing bed assignments, triage level, and current vitals
Electronic Medical Record (EMR) panel with patient history and pre-hospital notes
Touch-based order entry for labs, imaging, and treatments (as directed by supervising clinician)
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Cardiac monitor, oxygen supply, trauma intervention tray
Crash cart with emergency meds, airway tools, and defibrillator
PPE and sterile supplies
EMR documentation console
Medication administration tools (auto-injectors, IV pumps)
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Accuracy of clinical observations and timely reporting
Effective communication within the interdisciplinary team
Correct usage of hospital-grade equipment and workflows
Maintenance of patient safety and infection control standards
Appropriate escalation and situational prioritization
Imaging & Diagnostics – MRI Protocols
Scenario Type: Radiological safety and diagnostic support
Learning Level: Intermediate
Duration: 12–15 minutesScenario Overview
Trainees are guided through the preparation, support, and monitoring processes for a patient undergoing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This module teaches essential safety checks, communication strategies for patient reassurance, and the basics of collaborating with imaging technicians and interpreting initial results.The scenario simulates real-world MRI suite procedures and includes potential complications, such as patient anxiety or movement artifacts.Core Learning Objectives
MRI Safety Protocols:
Enforce strict no-metal policies, screen patients for contraindications (implants, pacemakers), and confirm completion of MRI safety checklists.Patient Communication & Preparation:
Provide clear instructions about the MRI process. Address claustrophobia or anxiety with empathy, and explain the importance of remaining still during the scan.Technical Collaboration:
Coordinate with imaging techs regarding the patient’s positioning, IV contrast administration (if applicable), and patient monitoring during scanning.Remote Observation & Intervention:
Monitor the patient during the scan via camera and audio interface. Identify signs of discomfort, respiratory distress, or equipment malfunction.Intro to Interpretation & Clinical Relevance:
Review imaging summaries post-scan. Identify common abnormalities (e.g., bleeds, fractures, swelling) and understand their implications for treatment plans.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
MRI control dashboard with scan progress bar, noise level indicators, and emergency stop
Pre-scan screening UI with implant/allergy checklists
Voice and video comm interface for real-time communication with the patient
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Full-body MRI machine with gurney
Non-magnetic transport equipment (IV stands, wheelchairs)
Contrast injection station with safety documentation
Patient comfort items (earplugs, pillows, anxiety-reducing visuals)
Monitoring tools (pulse oximeter, visual surveillance)
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Completion and accuracy of safety protocols
Communication clarity and effectiveness with the patient
Coordination with radiology team
Observation of patient comfort and safety throughout the scan
Preliminary understanding of diagnostic findings
Pre-Surgery Consultation & Preparation
Scenario Type: Pre-operative education, consent, and multidisciplinary planning
Learning Level: Intermediate to Advanced
Duration: 10–15 minutesScenario Overview
In this scenario, trainees participate in a surgical pre-consultation, where they assist in preparing a patient for an upcoming procedure. The focus is on effective communication, informed consent, patient reassurance, and coordination with the surgical and anesthesia teams.The simulation builds empathy, patient-centered care habits, and attention to procedural clarity—all vital for safe and ethical surgical preparation.Core Learning Objectives
Surgical Procedure Explanation:
Learn how to present information about the surgery in clear, accessible language. Understand how to describe the purpose, expected outcomes, and steps involved.Risk & Consent Communication:
Discuss common risks, potential complications, and anesthesia-related concerns. Ensure the patient understands and signs informed consent documents appropriately.Patient-Centered Communication:
Address the patient's emotional concerns with empathy. Clarify misconceptions, listen actively, and provide reassurance using appropriate tone and language.Collaboration with the Surgical Team:
Coordinate with surgeons, anesthesiologists, and pre-op nurses to ensure all preparations (labs, imaging, fasting protocols, allergy checks) are complete.Pre-op Checklist Compliance:
Confirm completion of required forms, medication reviews, and pre-operative clearance. Prepare the patient for physical and psychological readiness.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
Interactive patient education tablet with 3D visuals and procedural animations
Consent form signing system with alerts for missing items
Pre-op checklist interface (labs, allergies, fasting, clearance, COVID screen, etc.)
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
3D anatomical models to explain procedure sites
Educational handouts (diet, wound care, mobility aids post-surgery)
Surgery consent, anesthesia consent, and pre-op instructions forms
Digital EMR view of patient labs and clearance reports
Anxiety screening tools and emotional support prompts
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Clarity and accuracy in explaining surgical procedures
Patient engagement and understanding assessment
Professionalism and empathy in patient interactions
Compliance with pre-op protocols and documentation
Team coordination effectiveness with surgical staff
Robotic-Assisted Surgery Observation
Scenario Type: Operating room observation – robotic system integration
Learning Level: Advanced
Duration: 10–12 minutesScenario Overview
This simulation introduces trainees to a modern operating room environment equipped with a robotic-assisted surgical system (e.g., da Vinci Surgical System). Trainees observe how human expertise and robotic precision are combined for minimally invasive procedures.The scenario emphasizes interdisciplinary roles, sterile protocols, technological familiarity, and the broader workflow surrounding robotic surgeries—from setup to post-op planning.Core Learning Objectives
Understanding Robotic Surgical Workflow:
Observe how robotic-assisted procedures are initiated, controlled, and monitored by the lead surgeon, supported by a scrub team and circulating nurse.Roles in the OR:
Identify the responsibilities of each team member, including surgeons, anesthesiologists, surgical technologists, and nursing staff.Sterility & Equipment Awareness:
Learn proper sterile field etiquette, robot docking procedures, and safety measures related to robotic arms, visual consoles, and instrument trays.Technology Familiarization:
Understand the layout and controls of robotic systems, the role of the surgeon's console, and real-time monitoring of patient vitals and visual feeds.Observation for Post-op Planning:
Note key moments in the procedure that may influence recovery pathways (e.g., bleeding risk, tissue condition, surgical complexity).
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
Robotic system control panel (observation mode) with annotated visual overlay
Vital signs monitoring console with procedural synchronization
Live endoscopic view feed from robotic camera system
Medical & Surgical Props (Virtual):
da Vinci-style robotic arms and docking base
Surgeon's console and assistant station
OR monitors, light panels, and anesthetic workstation
Sterile drapes, laparoscopic toolkits, and specimen containers
Communication headsets for team coordination
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Identification of surgical team roles and functions
Understanding of robotic system purpose and workflow
Recognition of OR safety and sterile procedure standards
Ability to correlate observed procedure details to post-op care needs
Awareness of technological-human integration in surgical environments
Post-Operative Care & ICU Transition
Scenario Type: Immediate post-surgical critical care
Learning Level: Advanced
Duration: 15–20 minutesScenario Overview
Following a major surgical procedure, the trainee now transitions from observer to active caregiver in a simulated Intensive Care Unit (ICU) environment. The patient is in early post-operative recovery, requiring continuous monitoring, equipment management, and clear documentation. This phase emphasizes vigilance, teamwork, and timely response to instability or complications.The scenario simulates real-time shifts in vitals, alarms, and medication needs while requiring clinical judgment and emotional composure.Core Learning Objectives
ICU Monitoring & Equipment Handling:
Interpret and respond to data from ventilators, infusion pumps, and cardiac monitors. Adjust oxygenation, fluid rates, and sedation levels as per protocols or physician orders.Post-Op Assessment & Complication Recognition:
Conduct focused post-operative assessments. Identify early signs of infection, hemorrhage, pain escalation, respiratory distress, or neurological changes.Communication & Handoff:
Relay patient condition updates during shift changes, rounds, or deterioration events using structured formats (e.g., SOAP or SBAR).Family Communication & Emotional Support:
Deliver status updates and expectations to family members in a sensitive, compassionate manner. Clarify post-op progress and involve them in care planning when appropriate.Documentation & Care Planning:
Accurately chart vitals, administered meds, fluid balance, and nursing observations. Prepare input for daily care plans and multidisciplinary discussions.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
ICU bedside monitor with customizable vitals
IV/medication control dashboard with titration tools
Nursing documentation UI with progress notes and order sets
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Ventilator, cardiac monitor, and syringe pumps
Oxygen masks, trach care kits, IV setups
Post-op dressing and wound care tools
Emergency meds (e.g., vasopressors, pain control)
PPE for ICU-standard precautions
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Timeliness and accuracy in monitoring and responding to vital signs
Competence with ICU equipment and basic troubleshooting
Clarity and compassion in family communications
Accuracy of documentation and contributions to care plans
Recognition of clinical deterioration and escalation protocol adherence
Recovery Room Care & Discharge Preparation
Scenario Type: Post-operative stabilization, education, and discharge planning
Learning Level: Intermediate to Advanced
Duration: 12–15 minutesScenario Overview
Now in a post-surgical recovery suite, the patient is stable and gradually transitioning to lower-acuity care. Trainees must monitor for late complications, manage pain, begin early rehabilitation activities, and communicate clearly with the patient and their family about next steps.This scenario develops practical discharge planning skills, interdisciplinary coordination, and holistic care habits including physical, emotional, and social readiness for transition.Core Learning Objectives
Post-Operative Monitoring & Reassessment:
Monitor vitals, surgical wound sites, and mobility. Recognize subtle signs of delayed complications such as infection, DVT, or medication side effects.Pain & Comfort Management:
Assess pain using validated scales. Administer or coordinate analgesic regimens and non-pharmacological comfort techniques (e.g., positioning, breathing, heat packs).Early Rehabilitation & Education:
Support early ambulation or physical therapy routines. Educate the patient and caregivers on wound care, activity restrictions, medication adherence, and red flags.Discharge Planning & Interdisciplinary Coordination:
Contribute to discharge planning with PT/OT, case managers, and pharmacists. Understand timelines for follow-ups, home care referrals, and equipment needs.Psychosocial & Cultural Considerations:
Address emotional wellbeing, caregiver readiness, health literacy, and any language or cultural factors affecting the discharge process.
Equipment & Interface Highlights
Digital Interfaces:
Recovery tracker with pain scores, ambulation logs, and medication adherence
Discharge checklist UI (meds, equipment, education, referrals)
Interactive education module with instructional videos and printable guides
Medical & Safety Props (Virtual):
Pain management tools (oral meds, IV pumps, non-drug strategies)
Mobility aids (walker, cane, support belts)
Dressing materials, compression stockings, wound care kits
Teaching materials (brochures, models, handouts)
Medication pill organizer and home care checklist
Scenario Evaluation Metrics
Responsiveness to recovery progression and late complications
Effectiveness in pain and comfort support
Accuracy and clarity of patient education
Thoroughness of discharge planning steps
Respectful, person-centered communication with patients and families
Module 1: Emergency Response & Clinical Continuum
Accident Scene Discovery
On-Site Triage & Treatment
Ground Ambulance Preparation
Helicopter Evacuation Preparation
In-Flight Medical Care
In-Ambulance Care
Hospital Arrival & Transfer
Emergency Department Integration
Imaging & MRI Diagnostic Protocols
Pre-Surgery Consultation & Preparation
Robotic-Assisted Surgery Observation
Post-Operative Care & ICU Transition
Recovery Room & Discharge Planning
Pedagogical Foundations & Learning Objectives
Aligned with QSEN, NMC (UK), AACN Essentials
Simulation-based learning theory
Scenario realism vs. cognitive load balancing
Assessment criteria: decision-making, teamwork, clinical judgment
Technology & Delivery Infrastructure
Hardware requirements: VR headset, optional PC-based mode
Software deployment: local, cloud, LMS plugins
Instructor dashboard: real-time observation, analytics, debriefing tools
Data & Privacy compliance (HIPAA / GDPR-ready)